Overview
- Wavelength: 1 m - 5 Km
- Measures: Magnetic spin transitions
- Typical Uses: Organic molecules, Structure
- Key Formulae:
- Larmor Frequency:
- Chemical Shift:
- Larmor Frequency:
- Selection Rules:
Important Concepts
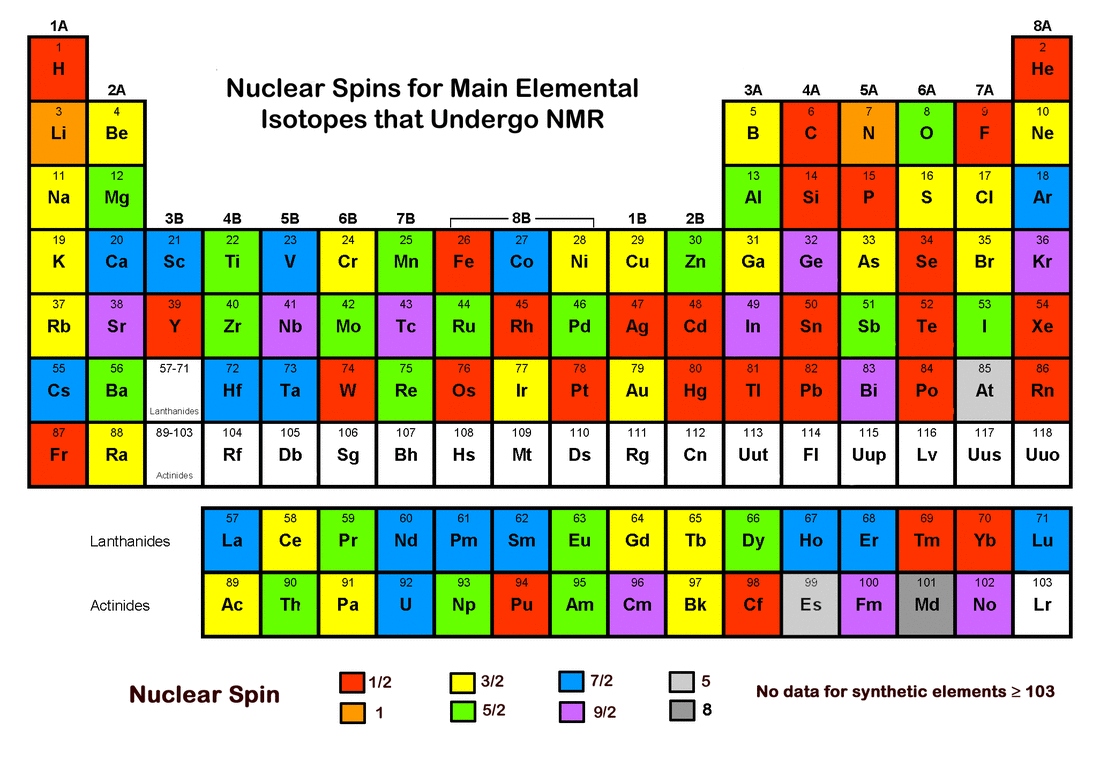
Spin Quantum Numbers
-
Total Spin Quantum Number (l):
- l = 0, 1/2, 1, 3/2, ...
- Proton/Neutron Combinations:
Protons Neutrons Spin Quantum Number (l) Even Even 0 Odd Odd 1, 2, 3, ... Even Odd 1/2, 3/2, 5/2, ... Odd Even 1/2, 3/2, 5/2, ...
-
Spin Angular Momentum Vector Magnitude:
-
Magnetic Quantum Number (m):
to -
Nuclear Magnetic Moment (
):
Energy and Polarization
- Energy Difference:
- Polarization:
- Boltzmann Distribution:
- Energy of Levels:
- Allowed Magnetic Dipole Transitions:
Larmor Frequency and Chemical Shift
- Larmor Frequency:
- Shifted Larmor Frequency:
- Chemical Shift (ppm):
- Frequency Separation (Hz):
- Receiver Reference Frequency (Rx):
Applications and Calculations
Calculating Impurity Concentration
- 13C Satellite Peaks:
- Integration of 13C peaks gives 0.5% relative to the proton peak. If impurity peaks integrate to less than a 13C peak, the impurity is less than 0.5% of the compound concentration.
NMR Limit of Detection (LOD)
- LOD Formula:
Sections to Explore
Visual Aids
- Element Nuclear Spin Quantum Numbers: