TLDR
- Wavelength: 0.0861 nm (14.4 keV)
- Measures: Energy gaps between nuclear states
- Uses: Detection of
, applicable only for solids - Selection Rules:
- Formula:
,
Light Source
-
Source Details:
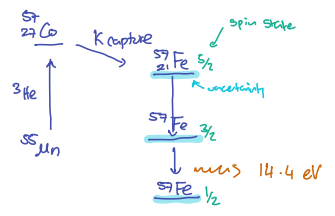
-photons are emitted from the nuclear decay of a radioactive mother isotope ( ). is typically produced via 3He bombardment of . - Decay of
results in a metastable excited state of , leading to a cascade of transitions, with one at keV, close to the absorbing energy for .
-
Energy Characteristics:
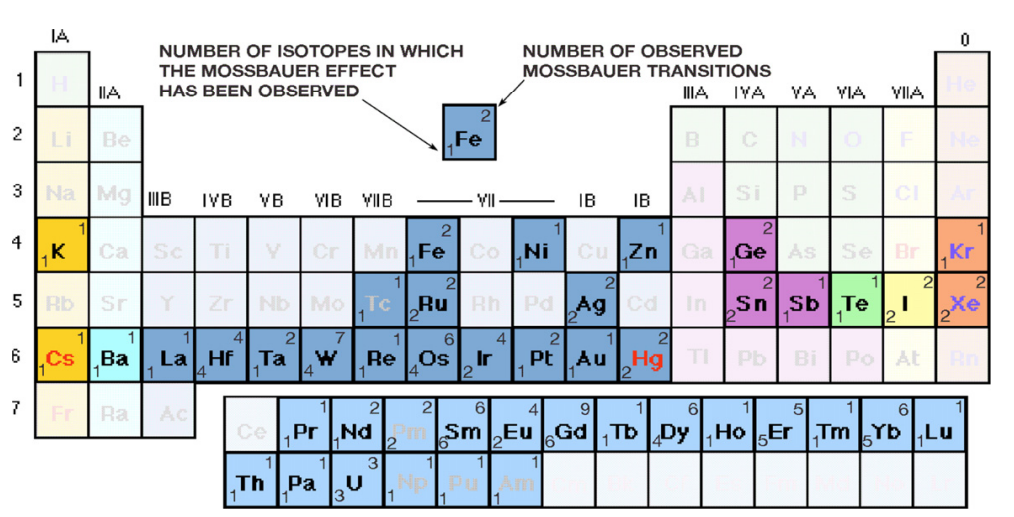
- The
excited state has a lifetime of 100 ns, leading to a very narrow energy width eV. - This narrow linewidth allows for selective detection of
in solids.
- The
Recoil Energy
-
Problem with Recoil Energy:
- The narrow width of
rays makes recoil energy significant, as photons transfer momentum to the nucleus, altering energy by an amount much larger than the Mössbauer linewidth.
- The narrow width of
-
Avoiding Recoil:
- Solids: In solids, molecular movement is restricted, reducing recoil effects.
- Zero-Phonon Processes: These processes have a higher probability in solids, leading to sharp lines. The probability factor is given by the [Lamb-Mössbauer factor (f)].
The Mössbauer Experiment
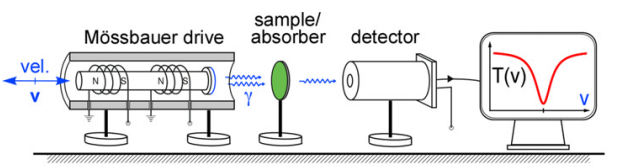
- Experiment Setup:
-
Components:
-
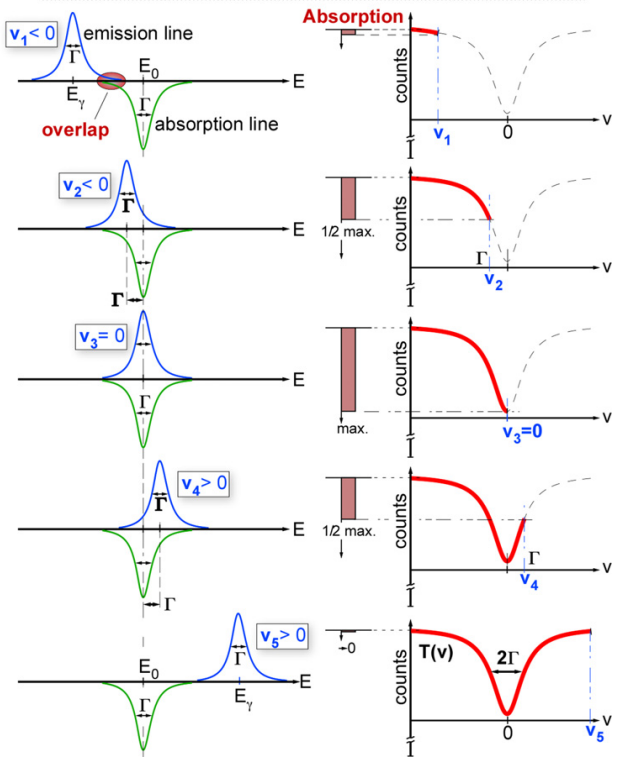
Doppler Effect Usage:
- Energy modulation is achieved by moving the source relative to the absorber, causing Doppler shifts in photon energy:
where is the source velocity.
-
Transmission Setup:
- A transmission arrangement is used:
- A transmission arrangement is used:
-
Experimental Process:
- The source is moved at Doppler velocities, and absorption probability is measured at each velocity by the overlap of the Doppler-shifted emission line with the absorption line.
-
Hyperfine Interactions
- Overview:
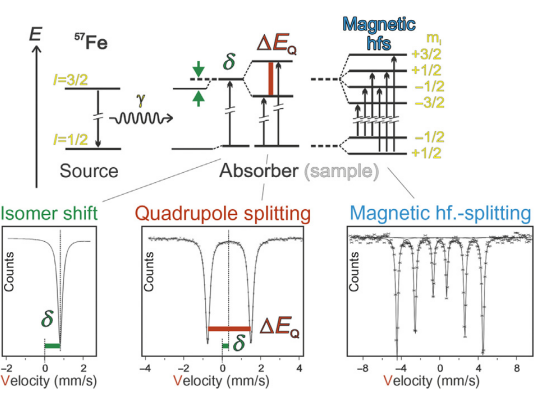
Isomer Shift
-
Description:
- Isomer shift occurs due to changes in the nuclear environment, typically relative to a reference (metallic iron).
-
Key Factors:
- Higher oxidation states result in shorter bond lengths and lower isomer shifts.
- High-spin states have higher isomer shifts than low-spin states.
- Four-coordination leads to shorter bond lengths and lower isomer shifts compared to six-coordination.
- Covalent bonds and complexes with soft ligands show lower isomer shifts.
Electric Quadrupole Interaction
-
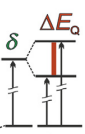
Description:
- Quadrupolar States: These states split into two due to the electric quadrupole interaction, with the ground state remaining unsplit.
-
Mechanism:
- Caused by the interaction of non-spherical nuclei with an inhomogeneous electric field from an asymmetric charge distribution of surrounding electrons.
Magnetic Hyperfine Splitting
- Description:
- Magnetic Field Influence: The application of a magnetic field lifts degeneracy due to the Zeeman Effect.
- Field Strength: Changing the field strength alters the Zeeman Effect, affecting the positions of the six peaks.