Key Definitions
- Symmetry operation: Actions that leave an object unchanged.
- Symmetry element: The axis, plane, or point where a symmetry operation occurs.
- Point group: A set of symmetry operations that describe an object's symmetry.
- Schoenflies symbols: Symbols denoting a point group.
- Group: A set of elements with the following properties:
- Associative multiplication:
- Closed group: The product of two group elements is within the group.
- Identity element: An element that leaves other elements unchanged.
- Inverse element: Every element has an inverse in the group, satisfying
.
- Associative multiplication:
- Abelian group: A group where all elements commute, i.e.,
. The Character table is symmetric along the diagonal. - Character table: A table showing the outcomes of all symmetry operation products in a group.
- Class: Symmetry operations that belong to the same class. If
, and are in the same class. - Example:
and are in the same class since
- Example:
- Group order: The total number of symmetry operations in a group. The number of Classes can be higher.
Symmetry Operations and Elements
| Symbol | Symmetry operation | Symmetry element | Matrix Representation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Identity Operation | All space | ||
| n-fold rotation | n-fold axis | ||
| Reflection | Mirror plane | ||
| Inversion | Centre of inversion | ||
| Improper rotation | n-fold rotation axis, inversion centre |
Character Tables
Basic Concepts
- Character tables represent how symmetry operations affect different molecular orbitals or coordinates.
- Irreducible representations are the fundamental blocks of character tables, corresponding to specific symmetry types.
- Mulliken Symbols: Used to label representations in character tables:
- A: Symmetric with the principal rotation axis.
- B: Asymmetric with the principal rotation axis.
- E: Double degenerate.
- T: Triple degenerate.
- g/u: Indicate symmetry (gerade) or asymmetry (ungerade) to inversion
. - Primes and double primes indicate symmetry (prime) or asymmetry (double prime) with respect to
.
Properties of Character Tables
- The number of irreducible representations equals the number of classes in the group.
- The sum of the squares of all dimensions of the irreps equals the order of the group.
- The sum of the squares of all characters of an irrep equals the order of the group.
- Characters of different representations are orthogonal to each other.
reducible representations
- A reducible representation can be expressed as a sum of irreducible representations (irreps).
- Reduction formula:
: Number of times irrep appears in the reducible representation. : Group order. : Coefficient of the respective symmetry element.
Determining Irreducible Representations
Steps to Find an Irreducible Representation
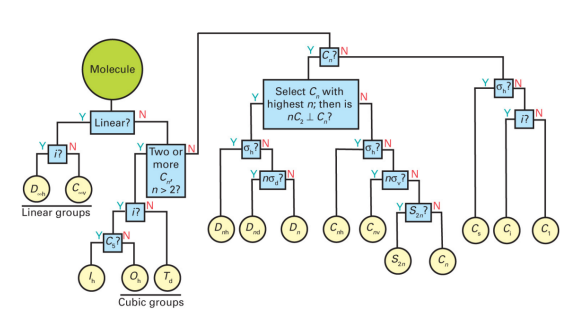
- Find the point group using flow charts or symmetry elements.
- Assign x, y, z coordinates to each atom.
- Determine atomic transformations under symmetry operations:
- Moving atom = 0
- Stationary atom = 1 for each unchanged axis, -1 for each inverted axis.
- Reduce the reducible representation to irreducible components using the reduction formula.
Examples
- N2O4 Example:
- Water Example:
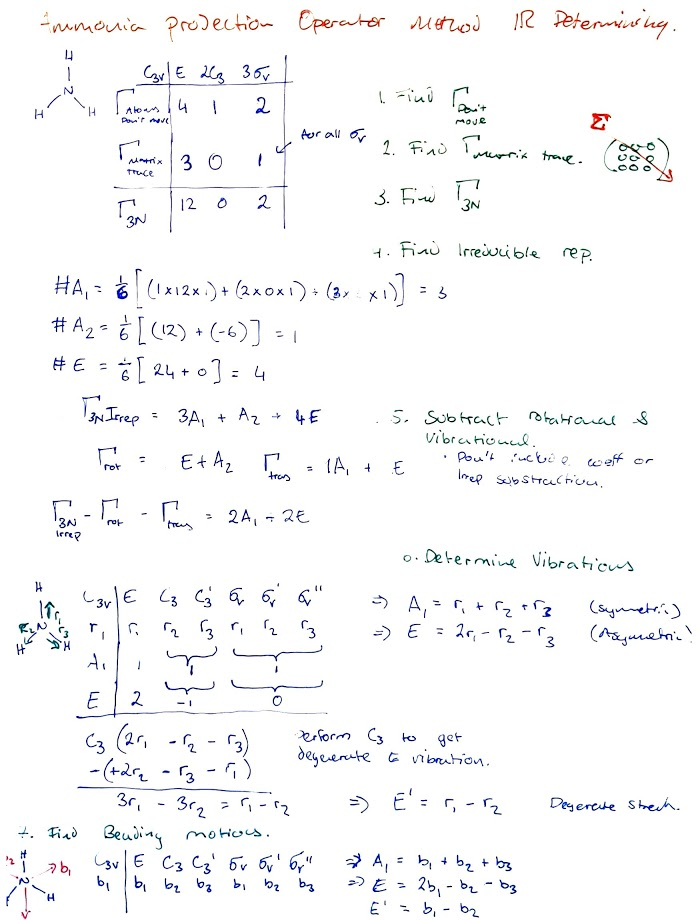
- Ammonia Example:
- Source video: {{youtube: https://youtu.be/vxwKbWz0m1o}}

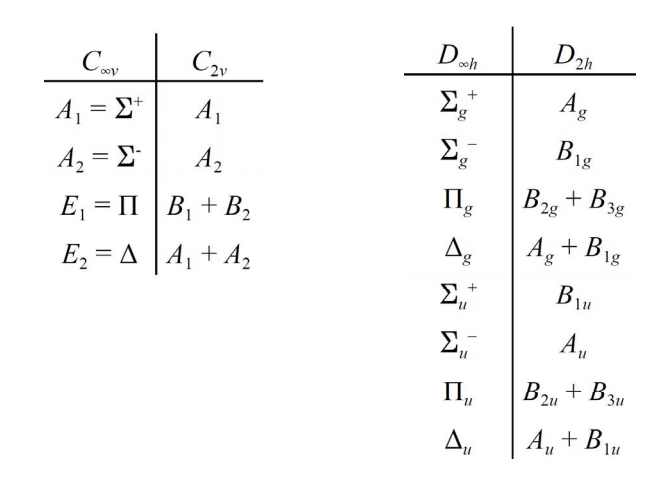
- For infinity groups:
- Solve the problem for a finite subgroup (e.g., C2v instead of C∞v).
- Use correlation tables to translate Schoenflies symbols to the infinity group.
- See SF2 Example:
Tools and Resources
- Spreadsheet Example: Link to Spreadsheet
- SALCs for Cyclobutadiene: Video Link
Symmetry Adapted Linear Combinations (SALCs)
Building SALCs
- Find the IRREP.
- Write the transformation (projection) of basis orbitals.
- Evaluate each IRREP contributor in terms of basis functions.
Example
IR and Raman Spectroscopy from Irreducible Representations
Overview
- Normal modes:
for non-linear molecules and for linear molecules.
Steps to Determine IR and Raman Activity
- Find the IRREP.
- Remove irreducible representations for translations and rotations.
- Determine IR and Raman active modes:
- IR activity: Requires a change in dipole moment (irreps such as
). - Raman activity: Requires a change in polarizability (quadratic functions).
- IR activity: Requires a change in dipole moment (irreps such as
Why Use Symmetry to Predict IR and Raman Modes?
- Normal coordinates and vibrational wavefunctions share symmetry properties, allowing predictions based on the character table.
Example
- Determining the IRREP of a Normal mode:
Electronic Spectroscopy Transitions
- The transition probability for an electronic transition can be determined using the dipole electric moment operator.
- For a transition to occur, the integral must be non-zero. Symmetry considerations can help us determine this.
Steps to Determine Electronic Transitions
- Determine the molecule point group.
- Draw or determine orbitals involved in the transition and determine their irreps.
- Determine the symmetries of different dipole moment operator bases.
- Find
for . - Transitions are allowed if the result is totally symmetric.
Allowedness of Transitions
-
Electronic transition:
can be any of the irreps related to the directions. - If the result is or contains a totally symmetric representation, the integral is non-zero, hence the transition is allowed.
- $A_1, A, A_g, A_{1g}, A^{\prime} $ all give non-zero integrals.
- The
that results in a symmetric representation indicates the required light polarization.
-
Vibronic transition:
- When an electronic transition is not allowed, a vibrational mode may make it allowed.
- The symmetry species of the mode multiplies the outcome of the electronic transition.
- If totally symmetric symmetry is found, the transition is vibronically allowed.
Example
- Vibronic Transition Example:
Translational Symmetry
Crystal Lattice
-
1D Lattice:
- There are 7 types of symmetry.
-
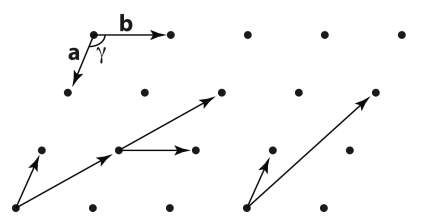
2D Lattice:
- Any pair of non-collinear translation vectors can be used to generate the lattice from one point.
- There are 5 types of symmetry classes for a 2D lattice.