- Measures: Different absorption of RCP and LCP due to chirality.
- Uses: Chirality.
- Formula:
- Selection Rules:
- Excellent website for visualizing light waves and CD.
- Wavelength: 300 - 190 nm.
- Basis:
- Relies on refraction of light, not absorbance.
- Absorption changes the light amplitude, not the frequency specdef.
- Refraction changes the frequency, not the amplitude specdef.
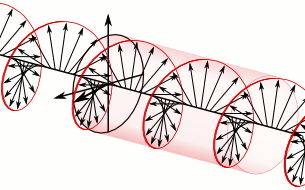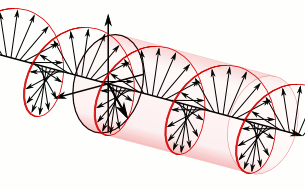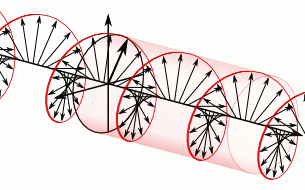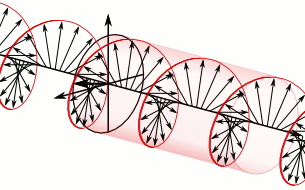
- Circularly polarized light can rotate in two directions.
- {{table}}
- Interaction
- Linear (Alignment)
- Circular (Chirality)
- Linear (Alignment)
- Refractive index
- Interaction
- Linear Dichroism (LD)
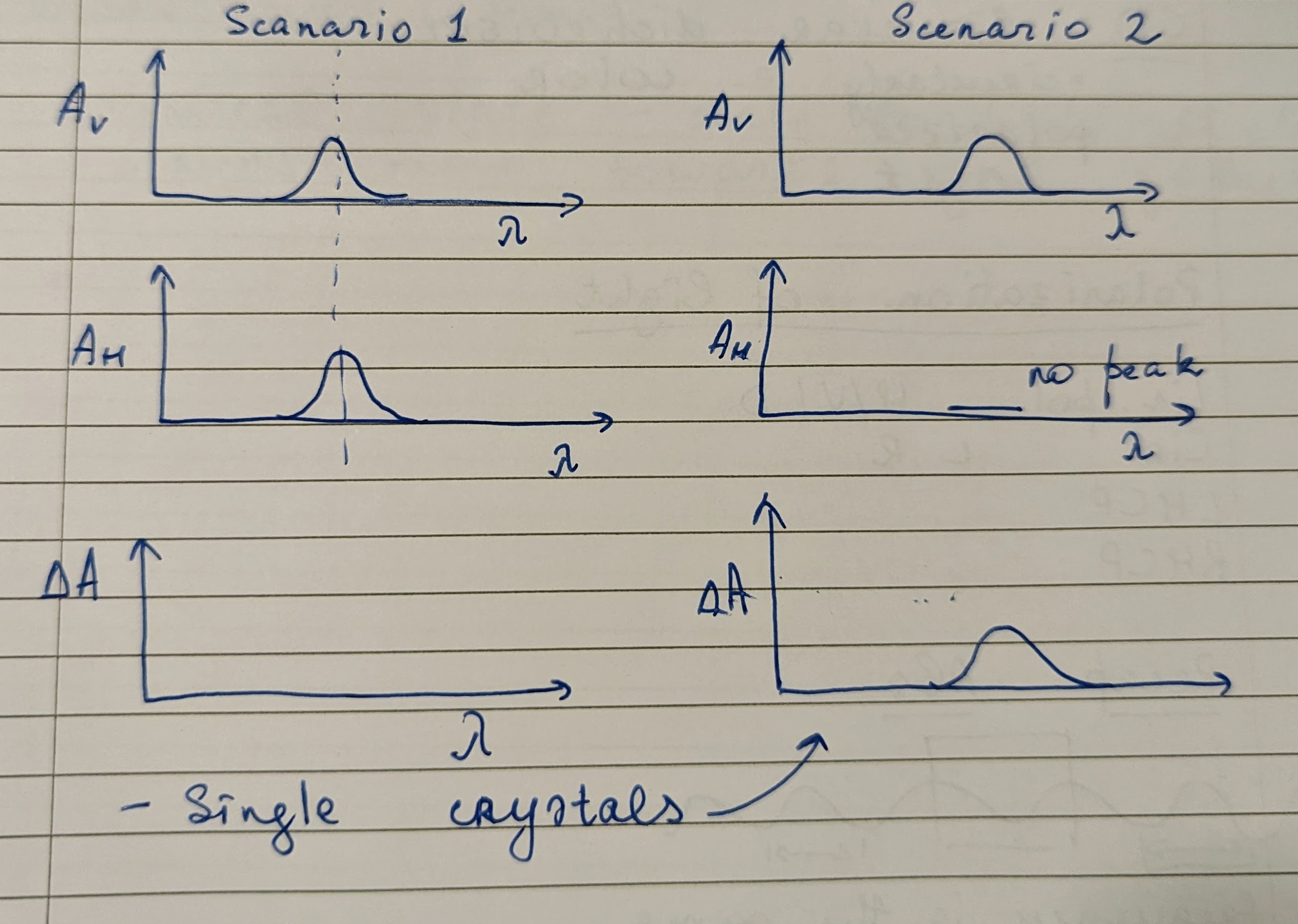
- Many aligned (Anisotropy) materials are linearly dichromic (LD). Hence, LD cannot be done on solutions.
- When many dipole moments are aligned, we observe linear dichroism. The molecules absorb light along the dipole moment axis.
where H and V indicate vertical and horizontal absorptions. - We are interested in seeing
as this is a measurable property and hence it needs to be non-zero, therefore Linear Dichroism (LD). - We measure horizontally and vertically polarized light separately.
- Flow chemistry or highly organized crystals can give alignment enough for LD spectroscopy.
- A DNA molecule gives horizontal but not vertical absorbance since the moment is along the backbone.
- Materials with different H and V refractive indexes are Birefringent specdef.
- Circular Dichroism (CD)
- Requirements: Differences in absorbance, chirality.
- The differential absorption between RCP and LCP light is measured.
-
CD tells us whether we have chiral samples, and quantum chemistry can be used to give R or S.
- Here we measure right and left polarized absorption:
.
Hence the Beer-Lambert Law. - We have opposite CD for R and S stereoisomers, and hence mirror image
plots in the form of a sine wave. - Energy gaps are different for RH and LH energy transitions, and therefore we get shifting in absorbances for these.
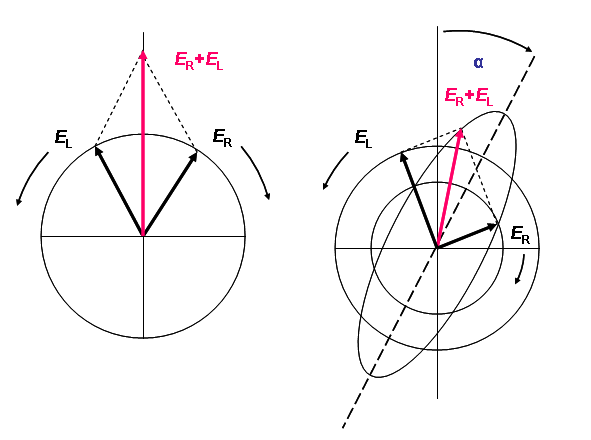
- Chiral molecules also have different refractive indices for RHCP and LHCP. This results in optical activity.
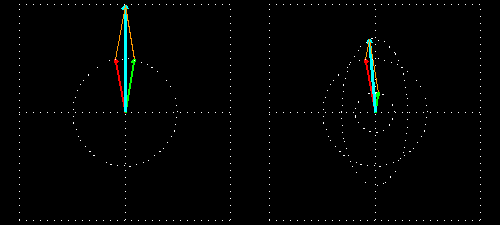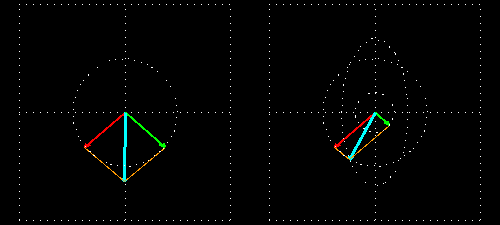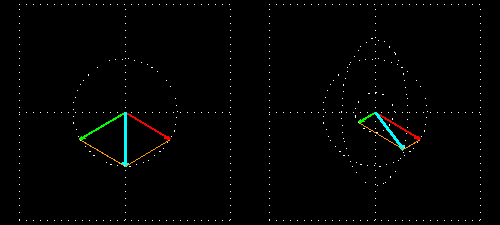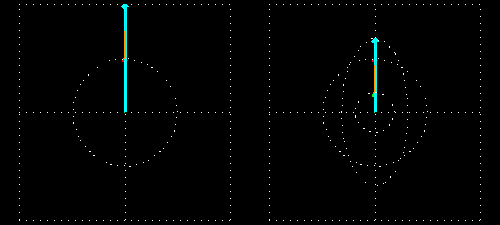
- Right: Two circularly polarized light waves of the same magnitude in an RCP and LCP mixture result in linearly polarized light.
- Left: The two waves after passing through an absorbing medium with different magnitudes between the waves, hence resulting in ellipticity.
- We can report the degree of ellipticity as
where E is the magnitude of the electric field vector (the light intensity). - Quantum mechanical basis:
- Method: